Related Vendors
Therefore, velocity gradient is introduced as a new feature of the clarifier. The particle size analysis of MLSS and plume indicated that natural flocculation occuring in the clarifier enhances efficiency of the system. The mean particle diameter of 40μm of MLSS 2.5 g/l was also observed to increase to 83μm within the plume.
Clarifier Process Makes Use of Natural Flocculation
The performance of the new system with respect to effluent suspended solids (SS) and returned activated sludge (RAS) concentrations, at an hour hydraulic retention time (HRT) for varying MLSS concentrations indicated that the Hydroplume can be effectively used for solid-liquid separation, having concentrations as low as 500 to as high as 5,000 mg/l.
Scale-up analysis of the system confirmed that its efficiency depends on many factors. The results of scale up formulations were validated through Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) studies. CFD studies of a full scale clarifier (Figure 3) 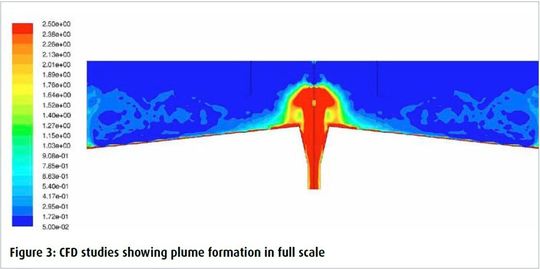
How to Achieve Minimum Hydraulic Retention in Waste–Water
Hydroplume is an effective secondary clarifier, which requires minimum hydraulic retention time (1–1.5 hours) and saves minimum of 25-30 per cent footprint area. Additionally, this indigenous technology offers the following advantages:
- As it does not require a separate flocculation facility, it reduces 35-40 per cent of capital and recurring costs while attaining high effluent quality standards
- The system ensures 98-99 per cent removal of suspended solids
- No separate pump house is required for sludge removal
:quality(80)/images.vogel.de/vogelonline/bdb/697100/697103/original.jpg)
TOC Analysis
How to Profit from TOC Analyzers — Reliable Monitoring of Water Quality
Solid-Liquid Separation in Domestic and Industrial Application
Hydroplume has high potential for use in domestic and industrial wastewater treatment systems. In water and wastewater treatment, solid-liquid separation is imperative and hence, use of the new system will enhance the functioning of treatment plants and make them more sustainable.It is also suitable for industrial application in sectors such as food, dairy, distillery, etc. In the food industry, many-a-time, chemicals are added to separate pulp from extracts.
(ID:42582617)



:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/77/1c/771c3d385d46ede7ab736f3f7d63cb62/0130007313v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/0b/33/0b3359449325c4e66cffdb41fce11683/0129956557v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/60/25/60259e0165560492b717049a5006b5d2/0129719891v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/40/8f/408f074f8094bca2cd9bb078e79eccb0/0129580192v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/93/9f/939fb603e5c2c60e52e4e92dd1de44e2/0129972638v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/0d/22/0d221bfb0debc81ac74afafc9cc632c2/0129972549v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/1d/da/1ddaee208ed26c1ad241f3b8fb216afe/0129956568v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/e9/14/e9149b52a5cf436e6fe6743e491037ac/0129926282v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/6b/3f/6b3f057c83c494e4732337d870d52b21/0130006927v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/df/cd/dfcd0c2e0eb4b554f956e0161ae08519/0129794328v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/74/af/74af2b65341eeee13a44bc85eb759596/0129839901v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/26/12/261210e5920899e5c35c4f905d3be8bd/0129399814v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/a6/84/a68477d4ef879cc9cedeae332ca57c49/0129893677v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/42/67/42671f576c7f8a1284b54bc8f92cce02/0129864175v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/f7/70/f770417abff565b1743068fa37d21266/0129833262v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/9f/7c/9f7cd6c9dcb679827c4c2c10f116c8b9/0129832882v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/be/e1/bee13b8d51a419b9b8f0685e2b9d47bf/0128917673v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/51/7a/517a4e83c5827663b4839f5ddb98f434/0128872953v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/d5/72/d5728578b35b72f365f5086bc1d068da/0128662441v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/a9/69/a96920e47e362a9cf0b9916b7ad3d30a/0128071795v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/c4/54/c454c7d8fd344c0ffc2ef5db00ad632f/0129728429v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/18/47/1847e6b1456c96f04bd511bbd21f3779/0129039479v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3b/fd/3bfda4bbcb1a60004c330bde3b705109/0128453300v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/cc/19/cc19aa5fec6f6f2b25dbd9516efed735/0128077403v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/6b/cc/6bcc3d26e1c7c74d90a10bc3ca296ae1/0128362351v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/24/c8/24c84ab6b1bcd24468a87820a07a85aa/0128194707v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/1d/3e/1d3e2788eb37c1e974f36337c8d33cb5/0128191010v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/19/76/1976928d7d0a2ed7c1eeba7ade8552c8/0126365603v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/1d/33/1d33cbe43461f24175e18aa01a426840/0129971592v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/e6/e1/e6e126a90647ced00f744126dd914531/0129956040v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/a7/f3/a7f381d9a908136cf391070bcb069eae/0129925612v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/f8/29/f8298429c1638b949a6f76346f6709c7/0118701710v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/07/24/07242664ab2b1c7841c9d9d0a127670c/0116045959.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/c9/79/c979a20b32395ddfa93fe7ead90578a0/0108386061.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/9e/5c/9e5c92d942ed046a27562d6e3d730c92/0103483548.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/2a/07/2a07c1b62903e380aa62e7a581d4a9d1/0129925640v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/16/3d/163da381529db3a47348a9440655529b/0125732969v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/e7/82/e782bbbf96e4971c22241d76e5de1720/0124855387v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/a8/4e/a84e8039a90a5cf4751d01ebcf6ba1a9/0127510172v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/17/c7/17c703445f134eb3d7ecc7918dda2762/0124596096v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/2a/2c/2a2cffc07f51019065387cd63241b5ce/0119463370v1.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/b1/7e/b17ea8c62ccafad1d1fb072d6199bbd6/0118578446.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/01/9b/019b59f3ef2e852ec5058ba18f323af2/0129651573v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/99/d2/99d2e5e83062b4cf2aa3dc0a60d15f23/0129624804v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/d1/a8/d1a83b822e16733380268322d033abdc/0129239584v2.jpeg)
:fill(fff,0)/images.vogel.de/vogelonline/companyimg/2000/2093/65.jpg)
:fill(fff,0)/images.vogel.de/vogelonline/companyimg/103000/103097/65.jpg)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/68/c8/68c815bc8fe81/prominent-logo-300x300.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/c1/ed/c1ed89188a8fdb351601e36204d4c38b/0125059797v2.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/ca/ae/caaeba5fe175e8897b288263ea6eb6d3/0128662705v3.jpeg)